
Industry News
Learn more about us through the industry
News
Properties and technology of platinum, palladium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and ruthenium
- Categories:News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2021-11-08 13:55
- Views:0
(Summary description)In the mineral deposit classification, the platinum group element mineral deposit belongs to the natural platinum subgroup, including natural element mineral deposits of iridium, rhodium, palladium and platinum.
Properties and technology of platinum, palladium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and ruthenium
(Summary description)In the mineral deposit classification, the platinum group element mineral deposit belongs to the natural platinum subgroup, including natural element mineral deposits of iridium, rhodium, palladium and platinum.
- Categories:News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2021-11-08 13:55
- Views:0
In the mineral deposit classification, the platinum group element mineral deposit belongs to the natural platinum subgroup, including natural element mineral deposits of iridium, rhodium, palladium and platinum. There is a widespread phenomenon of isomorphic replacement between them, and then a series of isomorphic mixed crystals are formed. Its composition often contains iron, copper, nickel, silver and other similar substances. When their content is high, they constitute the corresponding species.
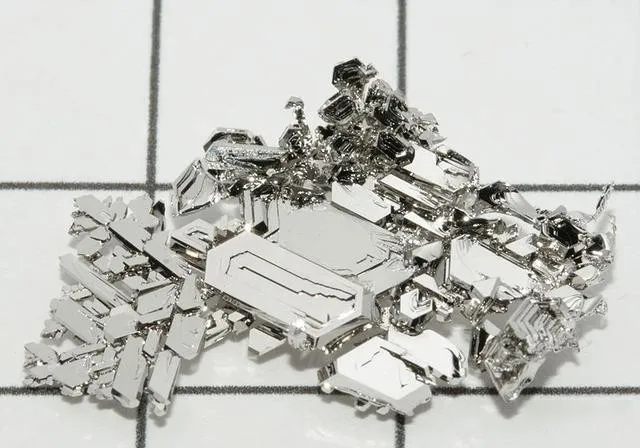
The platinum group elements are all equiaxed crystals, single crystals are rare, and sometimes cubic or octahedral fine crystal grains are produced. It is generally irregular granular, dendritic, grape-like or block-like in shape. The color and streaks range from snow white to steel gray, metallic luster, opaque, no cleavage, jagged fracture, ductile, and a long conductor of electricity and heat. The metals smelted from platinum group element minerals include palladium, iridium, platinum, rhodium, and so on.
1. Palladium: mainly smelted from natural tin. Snow white in color, similar in appearance to platinum, with metallic luster. Hardness 4~4.5. The relative density is 12. The melting point is 1555°C. The chemical properties are relatively stable. Because the output value is lower than platinum and yellow, it is of lower value and is rarely used to make jewelry.
2. Rhodium: mainly refined from natural rhodium, it is a sparse precious metal. The color is snow white, metallic luster, and opaque. Hard 4~4.5, relative density 12.5. The melting point is high at 1955°C. It is chemically stable. Because rhodium is corrosion-resistant and has good luster, it is mainly used in the electroplating industry. It is electroplated on the surface of other metals. The color of the coating is solid, not easy to wear, and has a good reflective effect.
3. Iridium: mainly extracted from natural iridium or our iridium ore. The color is snow white, with strong metallic luster, and the hardness is 7. The relative density is 22.40, it is brittle but can be pressed into foil or drawn into filaments at high temperature, and its melting point is high, reaching 2454℃. Chemical properties are very stable and insoluble in water. It is mainly used to make scientific instruments, thermocouples, resistors, etc. High-hardness iron-iridium and iridium-platinum alloys are often used to make pen nibs and platinum jewelry.
4. Platinum: It is made by smelting natural platinum, crude platinum ore and other mineral deposits. Because of the combination of platinum and platinum, the color is white again, so it is also called "Platinum". Snow white color, metallic luster, hardness 4~4.5, relative density 21.45. The melting point is high at 1773°C. High ductility, it can be drawn into very thin platinum wire and rolled into very thin platinum foil. The chemical property is extremely stable, insoluble in strong acid and strong acid, and does not oxidize in the air. It is widely used in the jewelry industry and the chemical industry to make high-end chemical utensils, platinum crucibles, and catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions.
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
Top dynamic rankings









2024-03-04

Scan the QR code and follow the official account
Products
Precious metal functional materials
High-quality optoelectronic materials/high-purity targets
Refractory metals and their alloys
Special alloy/special steel
Spherical | Nano powder
Biomedical/3D printing products
Compound
Rare metals and their alloys
Rare metals and their alloysRare Metal Concept Cultural/Art/Collectible
Nuclear energy Nuclear power Nuclear industry
High temperature heat container
Microelectronics industry Chip thermal sink
Semiconductor equipment MOCVD thermal field
High efficiency & long life Wire for wire cutting
Medical equipment Medical instruments
Artificial bone joint Bioimplantation
Rare metal cultural & creative art collection Precious metal
Plasma|Special Welding Electrode
Ultra Minor Metals Ltd (UMM) all rights reserved 湘ICP备17001881号 by:www.300.cnchangsha



